Tilted Empirical Risk Minimization
This repository contains the implementation for the paper
Tilted Empirical Risk Minimization
ICLR 2021
Empirical risk minimization (ERM) is typically designed to perform well on the average loss, which can result in estimators that are sensitive to outliers, generalize poorly, or treat subgroups unfairly. While many methods aim to address these problems individually, in this work, we explore them through a unified framework---tilted empirical risk minimization (TERM).
This repository contains the data, code, and experiments to reproduce our empirical results. We demonstrate that TERM can be used for a multitude of applications, such as enforcing fairness between subgroups, mitigating the effect of outliers, and handling class imbalance. TERM is not only competitive with existing solutions tailored to these individual problems, but can also enable entirely new applications, such as simultaneously addressing outliers and promoting fairness.
Getting started
Dependencies
As we apply TERM to a diverse set of real-world applications, the dependencies for different applications can be different.
- if we mention that the code is based on other public codebases, then one needs to follow the same setup of those codebases.
- otherwise, need the following dependencies (the latest versions will work):
- python3
- sklearn
- numpy
- matplotlib
- colorsys
- seaborn
- scipy
- cvxpy (optional)
Properties of TERM
Motivating examples
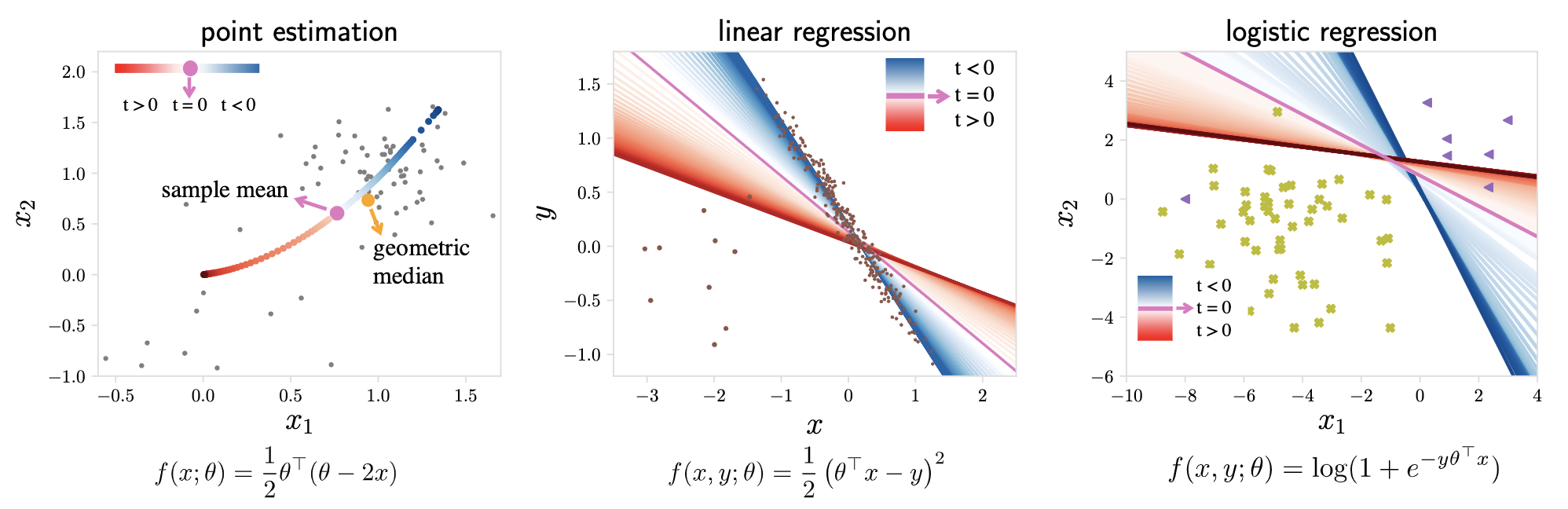
These figures illustrate TERM as a function of t: (a) finding a point estimate from a set of 2D samples, (b) linear regression with outliers, and (c) logistic regression with imbalanced classes. While positive values of t magnify outliers, negative values suppress them. Setting t=0 recovers the original ERM objective.
(How to generate these figures: cd TERM/toy_example & jupyter notebook , and directly run the three notebooks.)
A toy problem to visualize the solutions to TERM
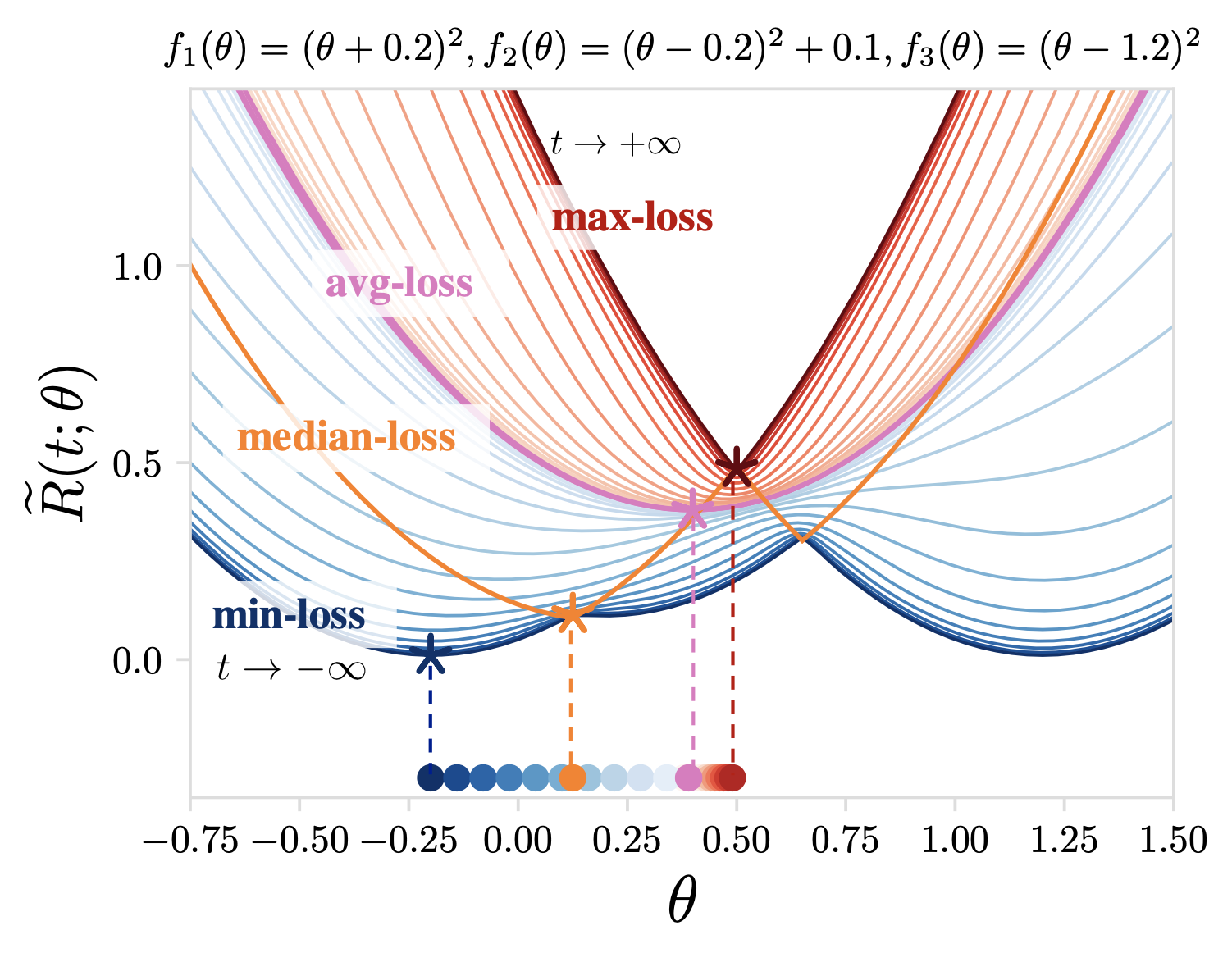
TERM objectives for a squared loss problem with N=3. As t moves from - to +
, t-tilted losses recover min-loss (t-->+
), avg-loss (t=0), and max-loss (t-->+
), and approximate median-loss (for some t). TERM is smooth for all finite t and convex for positive t.
(How to generate this figure: cd TERM/properties & jupyter notebook , and directly run the notebook.)
How to run the code for different applications
1. Robust regression
cd TERM/robust_regression
python regression.py --obj $OBJ --corrupt 1 --noise $NOISE
where $OBJ is the objective and $NOISE is the noise level (see code for options).
2. Robust classification
cd TERM/robust_classification
- built upon the public mentornet codebase
- dependencies: same as the dependencies of the mentornet codebase
- usage: see
READMEunderTERM/robust_classification
3. Mitigating noisy annotators
cd TERM/noisy_annotator/pytorch_resnet_cifar10
python trainer.py --t -2 # TERM
- built upon the public cifar10/cifar100 in pytorch codebase
- dependencies: same as the dependencies specified in the above codebase
4. Fair PCA
cd TERM/fair_pca
jupyter notebook
and directly run the notebook fair_pca_credit.ipynb.
- built upon the public fair pca codebase
- we directly extract the pre-processed Credit data dumped from the original matlab code, which are called
data.csv,A.csv, andB.csvsaved underTERM/fair_pca/multi-criteria-dimensionality-reduction-master/data/credit/. - dependencies: same as the fair pca code
5. Handling class imbalance
cd TERM/class_imbalance
python3 -m mnist.mnist_train_tilting --exp tilting # TERM, common class=99.5%
- built upon the public LearnReweight codebase
- dependencies: same as the LearnReweight code
6. Variance reduction for generalization
cd TERM/DRO
python variance_reduction.py --obj $OBJ $OTHER_PARAS
where $OBJ is the objective, and $OTHER_PARAS$ are the hyperparameters associated with the objective (see code for options). We report how we select the hyperparameters along with all hyperparameter values in Appendix E of the paper. For instance, for TERM with t=50, run the following:
python variance_reduction.py --obj tilting --t 50
simple_projections.pyis directly taken from the RobustRegRisk code
7. Fair federated learning
cd TERM/fair_flearn
bash run.sh tilting 0 0 term_t0.1_seed0 > term_t0.1_seed0 2>&1 &
- built upon the public q-FFL codebase
- download the vehicle dataset following the README in the q-FFL code
- dependencies: same as those required by the q-FFL code
8. Hierarchical multi-objective tilting
cd TERM/hierarchical
python mixed_level1.py --imbalance 1 --corrupt 1 --obj tilting --t_in -2 --t_out 10 # TERM_sc
python mixed_level2.py --imbalance 1 --corrupt 1 --obj tilting --t_in 50 --t_out -2 # TERM_ca
mixed_level1.py: TERM_{sc}: (sample level, class level)mixed_level2.py: TERM_{ca}: (class level, annotator level)
References
Please see the paper for more details of TERM as well as a complete list of related work.