Multimodal Temporal Context Network (MTCN)
This repository implements the model proposed in the paper:
Evangelos Kazakos, Jaesung Huh, Arsha Nagrani, Andrew Zisserman, Dima Damen, With a Little Help from my Temporal Context: Multimodal Egocentric Action Recognition, BMVC, 2021
Citing
When using this code, kindly reference:
@INPROCEEDINGS{kazakos2021MTCN,
author={Kazakos, Evangelos and Huh, Jaesung and Nagrani, Arsha and Zisserman, Andrew and Damen, Dima},
booktitle={British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC)},
title={With a Little Help from my Temporal Context: Multimodal Egocentric Action Recognition},
year={2021}}
NOTE
Although we train MTCN using visual SlowFast features extracted from a model trained with video clips of 2s, at Table 3 of our paper and Table 1 of Appendix (Table 6 in the arXiv version) where we compare MTCN with SOTA, the results of SlowFast are from [1] where the model is trained with video clips of 1s. In the following table, we provide the results of SlowFast trained with 2s, for a direct comparison as we use this model to extract the visual features.
Requirements
Project's requirements can be installed in a separate conda environment by running the following command in your terminal: $ conda env create -f environment.yml.
Features
The extracted features for each dataset can be downloaded using the following links:
EPIC-KITCHENS-100:
EGTEA:
Pretrained models
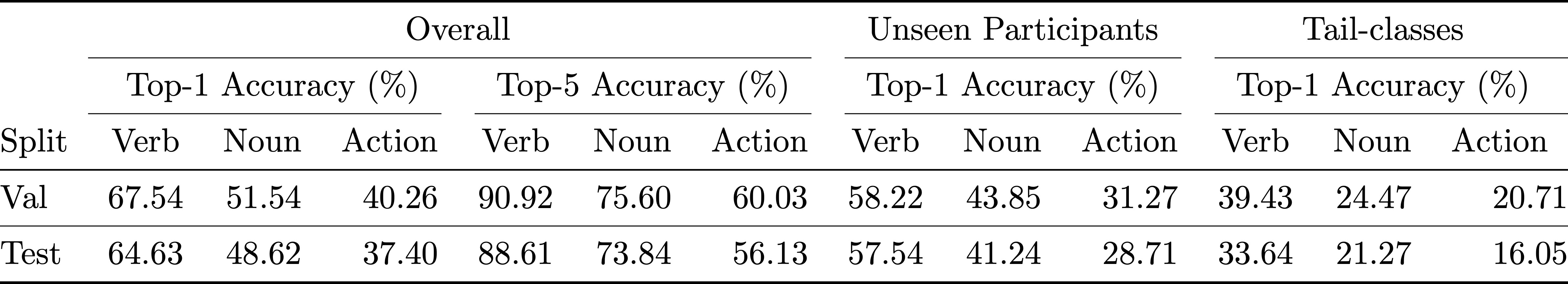
We provide pretrained models for EPIC-KITCHENS-100:
Ground-truth
- The ground-truth of EPIC-KITCHENS-100 can be found at this repository
- The ground-truth of EGTEA, processed by us to be in a cleaner format, can be downloaded from the following links: [Train-split1] [Test-split1] [Action mapping]
Train
EPIC-KITCHENS-100
To train the audio-visual transformer on EPIC-KITCHENS-100, run:
python train_av.py --dataset epic-100 --train_hdf5_path /path/to/epic-kitchens-100/features/audiovisual_slowfast_features_train.hdf5
--val_hdf5_path /path/to/epic-kitchens-100/features/audiovisual_slowfast_features_val.hdf5
--train_pickle /path/to/epic-kitchens-100-annotations/EPIC_100_train.pkl
--val_pickle /path/to/epic-kitchens-100-annotations/EPIC_100_validation.pkl
--batch-size 32 --lr 0.005 --optimizer sgd --epochs 100 --lr_steps 50 75 --output_dir /path/to/output_dir
--num_layers 4 -j 8 --classification_mode all --seq_len 9
To train the language model on EPIC-KITCHENS-100, run:
python train_lm.py --dataset epic-100 --train_pickle /path/to/epic-kitchens-100-annotations/EPIC_100_train.pkl
--val_pickle /path/to/epic-kitchens-100-annotations/EPIC_100_validation.pkl
--verb_csv /path/to/epic-kitchens-100-annotations/EPIC_100_verb_classes.csv
--noun_csv /path/to/epic-kitchens-100-annotations/EPIC_100_noun_classes.csv
--batch-size 64 --lr 0.001 --optimizer adam --epochs 100 --lr_steps 50 75 --output_dir /path/to/output_dir
--num_layers 4 -j 8 --num_gram 9 --dropout 0.1
EGTEA
To train the visual-only transformer on EGTEA (EGTEA does not have audio), run:
python train_av.py --dataset egtea --train_hdf5_path /path/to/egtea/features/visual_slowfast_features_train_split1.hdf5
--val_hdf5_path /path/to/egtea/features/visual_slowfast_features_test_split1.hdf5
--train_pickle /path/to/EGTEA_annotations/train_split1.pkl --val_pickle /path/to/EGTEA_annotations/test_split1.pkl
--batch-size 32 --lr 0.001 --optimizer sgd --epochs 50 --lr_steps 25 38 --output_dir /path/to/output_dir
--num_layers 4 -j 8 --classification_mode all --seq_len 9
To train the language model on EGTEA,
python train_lm.py --dataset egtea --train_pickle /path/to/EGTEA_annotations/train_split1.pkl
--val_pickle /path/to/EGTEA_annotations/test_split1.pkl
--action_csv /path/to/EGTEA_annotations/actions_egtea.csv
--batch-size 64 --lr 0.001 --optimizer adam --epochs 50 --lr_steps 25 38 --output_dir /path/to/output_dir
--num_layers 4 -j 8 --num_gram 9 --dropout 0.1
Test
EPIC-KITCHENS-100
To test the audio-visual transformer on EPIC-KITCHENS-100, run:
python test_av.py --dataset epic-100 --test_hdf5_path /path/to/epic-kitchens-100/features/audiovisual_slowfast_features_val.hdf5
--test_pickle /path/to/epic-kitchens-100-annotations/EPIC_100_validation.pkl
--checkpoint /path/to/av_model/av_checkpoint.pyth --seq_len 9 --num_layers 4 --output_dir /path/to/output_dir
--split validation
To obtain scores of the model on the test set, simply use --test_hdf5_path /path/to/epic-kitchens-100/features/audiovisual_slowfast_features_test.hdf5, --test_pickle /path/to/epic-kitchens-100-annotations/EPIC_100_test_timestamps.pkl and --split test instead. Since the labels for the test set are not available the script will simply save the scores without computing the accuracy of the model.
To evaluate your model on the validation set, follow the instructions in this link. In the same link, you can find instructions for preparing the scores of the model for submission in the evaluation server and obtain results on the test set.
Finally, to filter out improbable sequences using LM, run:
python test_av_lm.py --dataset epic-100
--test_pickle /path/to/epic-kitchens-100-annotations/EPIC_100_validation.pkl
--test_scores /path/to/audio-visual-results.pkl
--checkpoint /path/to/lm_model/lm_checkpoint.pyth
--num_gram 9 --split validation
Note that, --test_scores /path/to/audio-visual-results.pkl are the scores predicted from the audio-visual transformer. To obtain scores on the test set, use --test_pickle /path/to/epic-kitchens-100-annotations/EPIC_100_test_timestamps.pkl and --split test instead.
Since we are providing the trained models for EPIC-KITCHENS-100, av_checkpoint.pyth and lm_checkpoint.pyth in the test scripts above could be either the provided pretrained models or model_best.pyth that is the your own trained model.
EGTEA
To test the visual-only transformer on EGTEA, run:
python test_av.py --dataset egtea --test_hdf5_path /path/to/egtea/features/visual_slowfast_features_test_split1.hdf5
--test_pickle /path/to/EGTEA_annotations/test_split1.pkl
--checkpoint /path/to/v_model/model_best.pyth --seq_len 9 --num_layers 4 --output_dir /path/to/output_dir
--split test_split1
To filter out improbable sequences using LM, run:
python test_av_lm.py --dataset egtea
--test_pickle /path/to/EGTEA_annotations/test_split1.pkl
--test_scores /path/to/visual-results.pkl
--checkpoint /path/to/lm_model/model_best.pyth
--num_gram 9 --split test_split1
In each case, you can extract attention weights by simply including --extract_attn_weights at the input arguments of the test script.
References
[1] Dima Damen, Hazel Doughty, Giovanni Maria Farinella, , Antonino Furnari, Jian Ma,Evangelos Kazakos, Davide Moltisanti, Jonathan Munro, Toby Perrett, Will Price, andMichael Wray, Rescaling Egocentric Vision: Collection Pipeline and Challenges for EPIC-KITCHENS-100, IJCV, 2021
License
The code is published under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, found here.