To Startup
进入根目录(ner文件夹 或 seg_tag文件夹),执行:
pip install -r requirements.txt
等待环境配置完成
程序入口为main.py文件,执行:
python main.py
在seg_tag文件夹中将会一次性输出:
- 最大概率分词结果与P、R、F
- 最大概率分词(加法平滑)结果与P、R、F
- 最大概率分词(Jelinek-Mercer插值法平滑)结果与P、R、F
- 最短路分词结果与P、R、F
- 词性标注结果与两种评分的P、R、F
- 各算法耗时
在ner文件夹中将会输出:
- 各标签的数量和各自的P、R、F
- 测试集上的P、R、F
- 混淆矩阵
- 算法耗时
自动分词与词性标注部分
文件结构
D:.
│ clean.ipynb # 处理数据集
│ dag.py # 建图
│ dictionary.py # 建立词典
│ main.py # 程序入口
│ mpseg.py # 最大概率分词模块
│ pos.py # 词性标注模块
│ spseg.py # 最短路分词模块
│ requirements.txt
│ trie.py # trie树
│ score.py # 函数
│
├─data # 数据集
│ sequences.txt
│ wordpieces.txt
│
└─__pycache__
每个模块均经过单元测试和集成测试
代码注释采用Google风格
建立词典
定义class Trie作为词典数据结构,在Trie的尾节点保存该词出现的次数与词性。
使用Trie可以最大化节约空间开销。
定义class Dictionary作为词典,并统计词频、词性、转移矩阵、发射矩阵等。
基于词典的最短路分词
给定句子sentence[N],调用类SPseg中的spcut方法,代码依次执行:
- 依据词典建立有向无环图(调用类
DAG) - 最短路dp (调用
dp函数) - 回溯得到最短路径
- 返回分词结果
最短路分词获得的是尽可能小的分词集合。
基于统计的最大概率分词
给定句子sentence[N],调用类MPseg中的mpcut方法,代码依次执行:
- 依据词典建立有向无环图(调用类
DAG) - 根据类
Dictionary中统计的词频计算边权(边权为该词出现的概率) - 最短路dp (调用
dp函数) - 回溯得到最短路径
- 返回分词结果
最大概率分词得到的分词结果y满足 $$ y = argmax{P(y|x)} = argmax \frac{P(x|y)P(y)}{P(x)} $$ 其中$P(x), P(x|y)$是常数,即: $$ y & = argmax P(y|x)\ & = argmax P(y) \ & = argmax \prod_1^n P(w_i) \ & = argmax log(\prod_1^n P(w_i))\ & = argmin (- \sum_i^m log(P(w_i)) )\ $$ 最大概率即可等价于在DAG上求边权为$-log(P)$的最短路径
数据平滑
考虑到unseen event,对于频率为0的事件,我们也应分配一定的概率。
代码给出了两种数据平滑方式:
- Adding smoothing (加法平滑方法)
- Jelinek-Mercer interpolation (JM插值法)
Adding smoothing: $$ P(w_i) = \frac{\delta + c(w_i)}{\delta|V| + \sum_j c(w_j)} $$ 代码中取$\delta = 1$
Jelinek-Mercer interpolation $$ P(w_i) = \lambda P_{ML}(w_i) + (1-\lambda)P_{unif} $$ 思想为n元模型的概率由n元模型和n-1元模型插值而成
代码中取0元模型为均匀分布:$P_{unif} = \frac{1}{|V|}$,并给出$\lambda$的默认值为0.9
基于HMM的词性标注
HMM是一种概率图模型,基于统计学习得到emission matrix和transition matrix,推断给定观测序列(分词结果)的隐状态(词性序列)。
给出分词结果,调用类WordTagging中的tagging方法,代码依次执行:
- 根据词频计算发射概率和转移概率
- Viterbi decoding,找到具有最大概率的隐状态序列
- 回溯,得到隐状态序列
HMM经Viterbi解码得到的词性序列满足: $$ y & = argmax P(y|x)\ & = argmax \frac{P(y)P(x|y)}{P(x)} \ & = argmax P(y)\ & = argmax {\pi[t_i]b_1[w_1] \prod_1^{n-1} a[t_i][t_{i+1}]b_{i+1}[w_{i+1}]} \ & = argmax {log(\pi[t_i]b_1[w_1] \prod_1^{n-1} a[t_i][t_{i+1}]b_{i+1}[w_{i+1}])}\ & = argmin {-( log(\pi[t_i]) + log(b_1[w_1]) + \sum_i^m {log(a[t_i][t_{i+1}])+log(b_{i+1}[w_{i+1}])} )}\ $$
准确率、召回率、F1 score与性能
由公式: $$ P = \frac{系统输出的正确结果}{系统输出的全部结果个数} \ R = \frac{系统输出的正确结果}{测试集中的结果个数} \ F = \frac{2\times P \times R}{P+R} $$ 执行python main.py命令,在测试数据上推断,可得到上述全部分词、词性标注结果,并得到准确率、召回率、F1 score和性能指标
分词准确率:MP(with JM smoothing) = MP(with Add1 smoothing) > MP(no smoothing) = SP
使用平滑技术能得到更好的分词效果,统计方法(MP)比词典法能得到更好的分词效果。
HMM词性标注中,先利用MP(with JM smoothing) 法分词,再对分词结果进行词性标注。同时采用了粗略的评价指标(不考虑顺序)和严格的评价指标(考虑顺序)。
对于给定的长为N的序列:
| Methods | Inference Time Complexity |
|---|---|
| MP分词 | $O(N+M)$ |
| SP分词 | $O(N+M)$ |
| HMM词性标注 | $O(T^2N)$ |
其中,$M$为DAG中的边数,$T$词性总数。因此三个算法的推断复杂度都是线性的。
命名实体识别部分
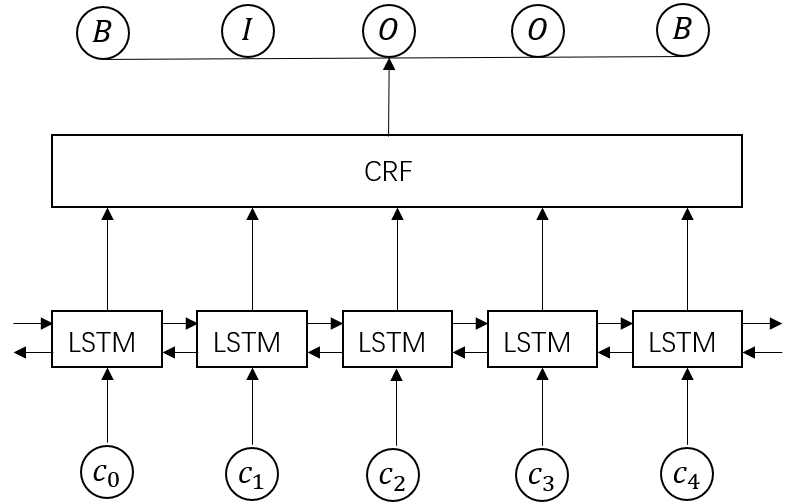
采用BiLSTM+CRF模型
其中,BiLSTM输入是给定的sentence(embedding sequence),输出为该词对应的命名实体标签。它通过双向的设置学习到观测序列(输入的字)之间的依赖,在训练过程中,LSTM能够根据目标(比如识别实体)自动提取观测序列的特征。但是,BiLSTM无法学习到输出序列之间的依赖与约束关系。
CRF等同于在BiLSTM的输出上添加了一层约束,使得模型也能学习到输出序列内部之间的的依赖。传统的CRF需要人为给出特征模板,但在该模型中,特征函数将由模型自行学习得到。
文件结构
D:.
│ dataloader.py # 载入数据集
│ evaluation.py # 评估模型
│ main.py # 程序入口
│ model.py # BiLSTM、BiLSTM+CRF模型
│ utils.py # 函数
│ requirements.txt
│
├─data_ner # 数据集
│ dev.char.bmes
│ test.char.bmes
│ train.char.bmes
│
├─results # 训练好的模型
│ BiLSTM+CRF.pkl
│
└─__pycache__
参数设置
| Total epoches | Batch size | learning rate | hidden size | embedding size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 64 | 0.001 | 128 | 128 |
每结束一个epoch,模型在验证集上评估,选取在验证集上效果最好的模型作为最终模型(optimal model)。
模型在测试集上能达到95%以上的准确率。
Reference
[1] 宗成庆 《统计自然语言处理》
[2] Lample G, Ballesteros M, Subramanian S, et al. Neural architectures for named entity recognition[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.01360, 2016.
[3] blog: 1. Understanding LSTM Networks -- colah's blog, 2. CRF Layer on the Top of BiLSTM - 1 | CreateMoMo
[4] code: 1. hiyoung123/ChineseSegmentation: 中文分词 (github.com) ,2. luopeixiang/named_entity_recognition: 中文命名实体识别(github.com), 3. Advanced: Making Dynamic Decisions and the Bi-LSTM CRF — PyTorch Tutorials 1.9.1+cu102 documentation
[5] dataset: 1. jiesutd/LatticeLSTM: Chinese NER using Lattice LSTM. Code for ACL 2018 paper. (github.com), 2. 人民日报1998