CinnaMon
CinnaMon is a Python library which offers a number of tools to detect, explain, and correct data drift in a machine learning system. At its core, CinnaMon allows to study data drift between two given datasets. It is particularly useful in a monitoring context where the first dataset is the training (or validation) data and the second dataset is the production data.
⚡️
Quickstart
As a quick example, let's illustrate the use of CinnaMon on the breast cancer data where we voluntarily introduce some data drift.
Setup the data and build a model
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> from sklearn import datasets
>>> from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
>>> from xgboost import XGBClassifier
# load breast cancer data
>>> dataset = datasets.load_breast_cancer()
>>> X = pd.DataFrame(dataset.data, columns = dataset.feature_names)
>>> y = dataset.target
# split data in train and valid dataset
>>> X_train, X_valid, y_train, y_valid = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=2021)
# introduce some data drift in valid by filtering with 'worst symmetry' feature
>>> y_valid = y_valid[X_valid['worst symmetry'].values > 0.3]
>>> X_valid = X_valid.loc[X_valid['worst symmetry'].values > 0.3, :].copy()
# fit a XGBClassifier on the training data
>>> clf = XGBClassifier(use_label_encoder=False)
>>> clf.fit(X=X_train, y=y_train, verbose=10)
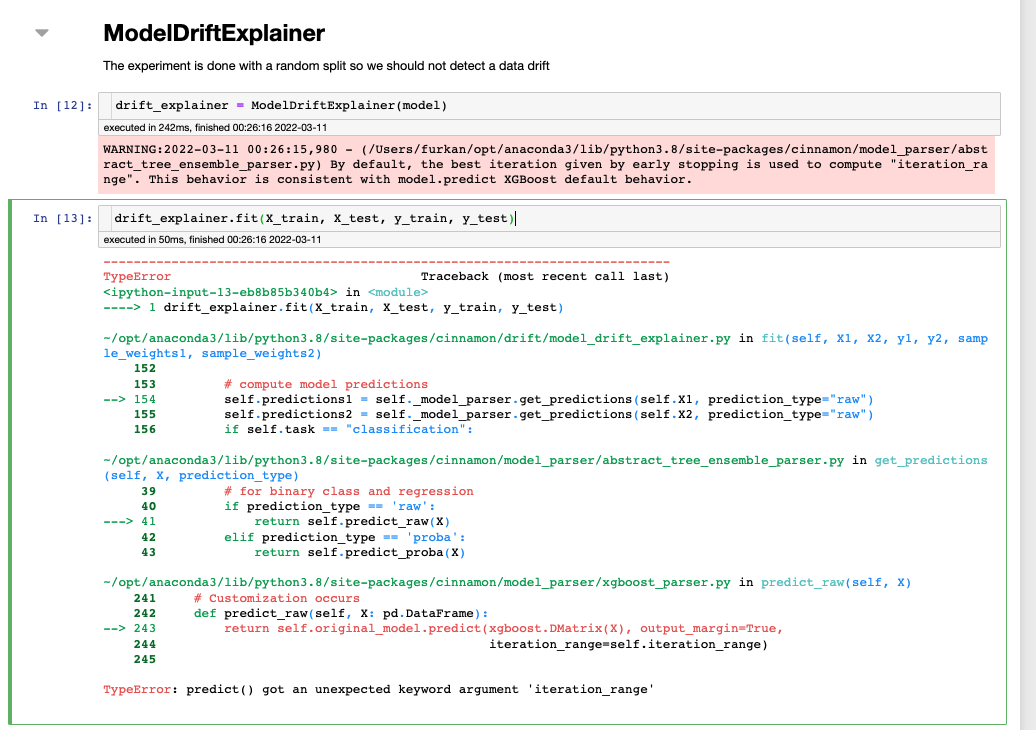
Initialize ModelDriftExplainer and fit it on train and validation data
>>> from cinnamon.drift import ModelDriftExplainer
# initialize a drift explainer with the built XGBClassifier and fit it on train
# and valid data
>>> drift_explainer = ModelDriftExplainer(model=clf)
>>> drift_explainer.fit(X1=X_train, X2=X_valid, y1=y_train, y2=y_valid)
Detect data drift by looking at main graphs and metrics
# Distribution of logit predictions
>>> drift_explainer.plot_prediction_drift(bins=15)
We can see on this graph that because of the data drift we introduced in validation data the distribution of predictions are different (they do not overlap well). We can also compute the corresponding drift metrics:
# Corresponding metrics
>>> drift_explainer.get_prediction_drift()
[{'mean_difference': -3.643428434667366,
'wasserstein': 3.643428434667366,
'kolmogorov_smirnov': KstestResult(statistic=0.2913775225333014, pvalue=0.00013914094110123454)}]
Comparing the distributions of predictions for two datasets is one of the main indicator we use in order to detect data drift. The two other indicators are:
- distribution of the target (see
get_target_drift) - performance metrics (see
get_performance_metrics_drift)
Explain data drift by computing the drift values
Drift values can be thought as equivalent of feature importance but in terms of data drift.
# plot drift values
>>> drift_explainer.plot_tree_based_drift_values(n=7)
Here the feature worst symmetry is rightly identified as the one which contributes the most to the data drift.
More
See "notes" below to explore all the functionalities of CinnaMon.
🛠
Installation
CinnaMon is intended to work with Python 3.9 or above. Installation can be done with pip:
pip install cinnamon
🔗
Notes
-
The two main classes of CinnaMon are
ModelDriftExplainerandAdversarialDriftExplainer -
ModelDriftExplainercurrently only supportXGBoostmodels (both regression and classification are supported) -
See notebooks in the
examples/directory to have an overview of all functionalities. Notably:These two notebooks also go deeper into the topic of how to correct data drift, making use of
AdversarialDriftExplainer -
See also the slide presentation of the CinnaMon library.
-
There is (yet) no formal documentation for CinnaMon but docstrings are up to date for the two main classes.
👍
Contributing
Check out the contribution section.
📝
License
CinnaMon is free and open-source software licensed under the MIT.