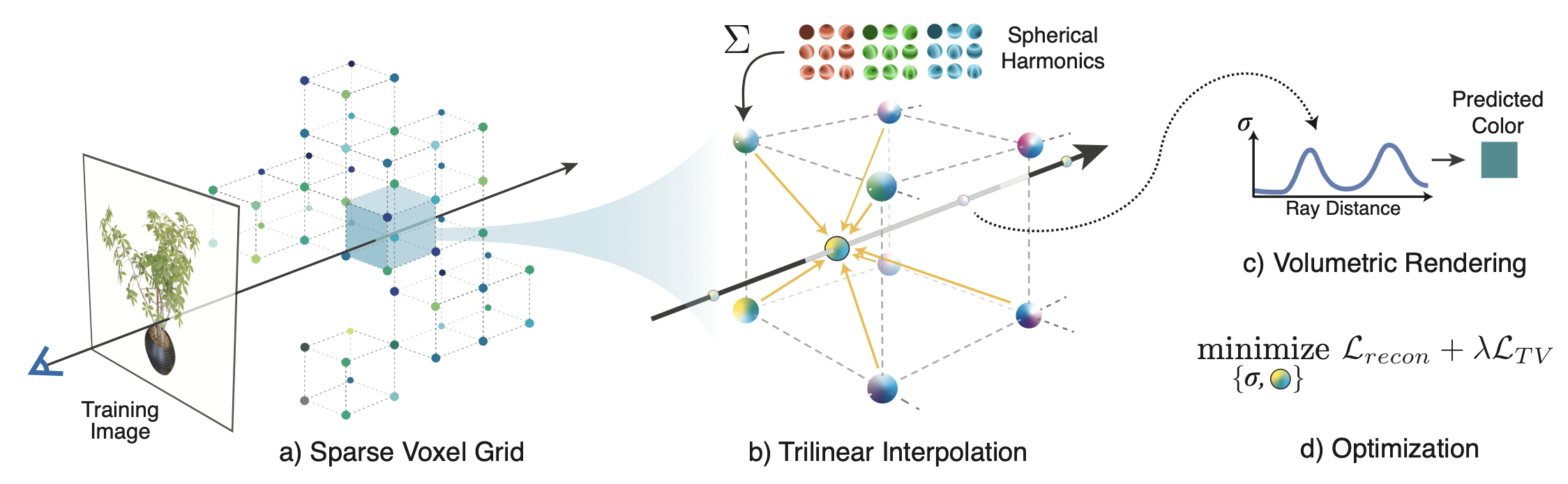
Plenoxels: Radiance Fields without Neural Networks
Alex Yu*, Sara Fridovich-Keil*, Matthew Tancik, Qinhong Chen, Benjamin Recht, Angjoo Kanazawa
UC Berkeley
Website and video: https://alexyu.net/plenoxels
arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.05131
Note: This is a preliminary release. We have not carefully tested everything, but feel that it would be better to first put the code out there.
Also, despite the name, it's not strictly intended to be a successor of svox
Citation:
@misc{yu2021plenoxels,
title={Plenoxels: Radiance Fields without Neural Networks},
author={{Alex Yu and Sara Fridovich-Keil} and Matthew Tancik and Qinhong Chen and Benjamin Recht and Angjoo Kanazawa},
year={2021},
eprint={2112.05131},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
This contains the official optimization code. A JAX implementation is also available at https://github.com/sarafridov/plenoxels. However, note that the JAX version is currently feature-limited, running in about 1 hour per epoch and only supporting bounded scenes (at present).
Setup
First create the virtualenv; we recommend using conda:
conda env create -f environment.yml
conda activate plenoxel
Then clone the repo and install the library at the root (svox2), which includes a CUDA extension.
If your CUDA toolkit is older than 11, then you will need to install CUB as follows: conda install -c bottler nvidiacub. Since CUDA 11, CUB is shipped with the toolkit.
To install the main library, simply run
pip install .
In the repo root directory.
Getting datasets
We have backends for NeRF-Blender, LLFF, NSVF, and CO3D dataset formats, and the dataset will be auto-detected. Please get the NeRF-synthetic and LLFF datasets from:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/128yBriW1IG_3NJ5Rp7APSTZsJqdJdfc1
We provide a processed Tanks and temples dataset (with background) in NSVF format at: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1PD4oTP4F8jTtpjd_AQjCsL4h8iYFCyvO/view?usp=sharing
Note this data should be identical to that in NeRF++
Voxel Optimization (aka Training)
For training a single scene, see opt/opt.py. The launch script makes this easier.
Inside opt/, run ./launch.sh <exp_name> <GPU_id> <data_dir> -c <config>
Where <config> should be configs/syn.json for NeRF-synthetic scenes, configs/llff.json for forward-facing scenes, and configs/tnt.json for tanks and temples scenes, for example.
The dataset format will be auto-detected from data_dir. Checkpoints will be in ckpt/exp_name.
Evaluation
Use opt/render_imgs.py
Usage, (in opt/) python render_imgs.py <CHECKPOINT.npz> <data_dir>
By default this saves all frames, which is very slow. Add --no_imsave to avoid this.
Rendering a spiral
Use opt/render_imgs_circle.py
Usage, (in opt/) python render_imgs_circle.py <CHECKPOINT.npz> <data_dir>
Parallel task executor
We provide a parallel task executor based on the task manager from PlenOctrees to automatically schedule many tasks across sets of scenes or hyperparameters. This is used for evaluation, ablations, and hypertuning See opt/autotune.py. Configs in opt/tasks/*.json
For example, to automatically train and eval all synthetic scenes: you will need to change train_root and data_root in tasks/eval.json, then run:
python autotune.py -g '<space delimited GPU ids>' tasks/eval.json
For forward-facing scenes
python autotune.py -g '<space delimited GPU ids>' tasks/eval_ff.json
For Tanks and Temples scenes
python autotune.py -g '<space delimited GPU ids>' tasks/eval_tnt.json
Using a custom image set
First make sure you have colmap installed. Then
(in opt/) bash scripts/proc_colmap.sh <img_dir>
Where <img_dir> should be a directory directly containing png/jpg images from a normal perspective camera. For custom datasets we adopt a data format similar to that in NSVF https://github.com/facebookresearch/NSVF
You should be able to use this dataset directly afterwards. The format will be auto-detected.
To view the data use: python scripts/view_data.py <img_dir>
This should launch a server at localhost:8889
You may need to tune the TV. For forward-facing scenes, often making the TV weights 10x higher is helpful (configs/llff_hitv.json). For the real lego scene I used the config configs/custom.json.
Random tip: how to make pip install faster for native extensions
You may notice that this CUDA extension takes forever to install. A suggestion is using ninja. On Ubuntu, install it with sudo apt install ninja-build. Then set the environment variable MAX_JOBS to the number of CPUS to use in parallel (e.g. 12) in your shell startup script. This will enable parallel compilation and significantly improve iteration speed.