Depthstillation
Demo code for "Learning optical flow from still images", CVPR 2021.
[Project page] - [Paper] - [Supplementary]
This code is provided to replicate the qualitative results shown in the supplementary material, Sections 2-4. The code has been tested using Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, python 3.8 and gcc 9.3.0
Reference
If you find this code useful, please cite our work:
@inproceedings{Aleotti_CVPR_2021,
title = {Learning optical flow from still images},
author = {Aleotti, Filippo and
Poggi, Matteo and
Mattoccia, Stefano},
booktitle = {IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
year = {2021}
}
Contents
Introduction
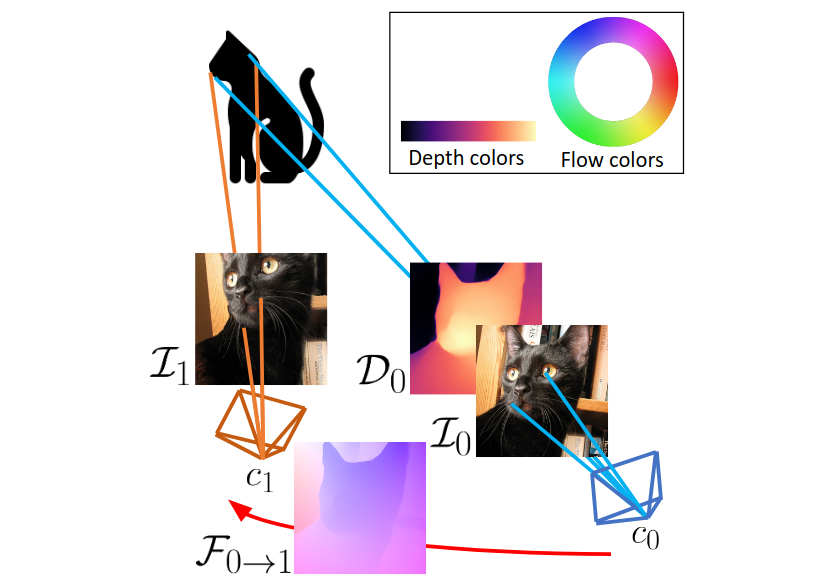
This paper deals with the scarcity of data for training optical flow networks, highlighting the limitations of existing sources such as labeled synthetic datasets or unlabeled real videos. Specifically, we introduce a framework to generate accurate ground-truth optical flow annotations quickly and in large amounts from any readily available single real picture. Given an image, we use an off-the-shelf monocular depth estimation network to build a plausible point cloud for the observed scene. Then, we virtually move the camera in the reconstructed environment with known motion vectors and rotation angles, allowing us to synthesize both a novel view and the corresponding optical flow field connecting each pixel in the input image to the one in the new frame. When trained with our data, state-of-the-art optical flow networks achieve superior generalization to unseen real data compared to the same models trained either on annotated synthetic datasets or unlabeled videos, and better specialization if combined with synthetic images.
Usage
Install the project requirements in a new python 3 environment:
virtualenv -p python3 learning_flow_env
source learning_flow_env/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
Compile the forward_warping module, written in C (required to handle warping collisions):
cd external/forward_warping
bash compile.sh
cd ../..
You are now ready to run the depthstillation.py script:
python depthstillation.py
By switching some parameters you can generate all the qualitatives provided in the supplementary material.
These parameters are:
num_motions: changes the number of virtual motionssegment: enables instance segmentation (for independently moving objects)mask_type: mask selection. Options areH'andHnum_objects: sets the number of independently moving objects (one, in this example)no_depth: disables monocular depth and force depth to assume a constant valueno_sharp: disables depth sharpeningchange_k: uses different intrinsicsKchange_motion: samples a different motion (ignored ifnum_motionsgreater than 1)
For instance, to simulate a different K settings, just run:
python depthstillation.py --change_k
The results are saved in dCOCO folder, organized as follows:
depth_color:colored depth mapflow: generated flow labels (in 16bit KITTI format)flow_color: colored flow labelsH: H maskH': H' maskim0: real input imageim1: generated virtual imageim1_raw: generated virtual image (pre-inpainting)instances_color: colored instance map (if--segmentis enabled)M: M maskM': M' maskP: P mask
We report the list of files used to depthstill dCOCO in samples/dCOCO_file_list.txt
Supplementary
We report here the list of commands to obtain, in the same order, the Figures shown in Sections 2-4 of the Supplementary Material:
- Section 2 -- the first figure is obtained with default parameters, then we use
--no_depthand--no_depth --segmentrespectively - Section 3 -- the first figure is obtained with
--no_sharp, the remaining figures with default parameters or by setting--mask_type "H". - Section 4 -- we show three times the results obtained by default parameters, followed respectively by figures generated using
--change_k,--change_motionand--segmentindividually.
Weights
We provide RAFT models trained in our experiments. To run them and reproduce our results, please refer to RAFT repository:
- Tab. 4 (C) dCOCO (D) Ch->Th->dCOCO
- Tab. 5 (C) dCOCO (fine-tuned) (D) Ch->Th->dCOCO (fine-tuned)
- Tab. 7 (C) dDAVIS
- Tab. 8 (C) dKITTI
Contacts
m [dot] poggi [at] unibo [dot] it
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Clément Godard and Niantic for sharing monodepth2 code, used to simulate camera motion.
Our work is inspired by Jamie Watson et al., Learning Stereo from Single Images.