Plux
plux is the dynamic code loading framework used in LocalStack.
Overview
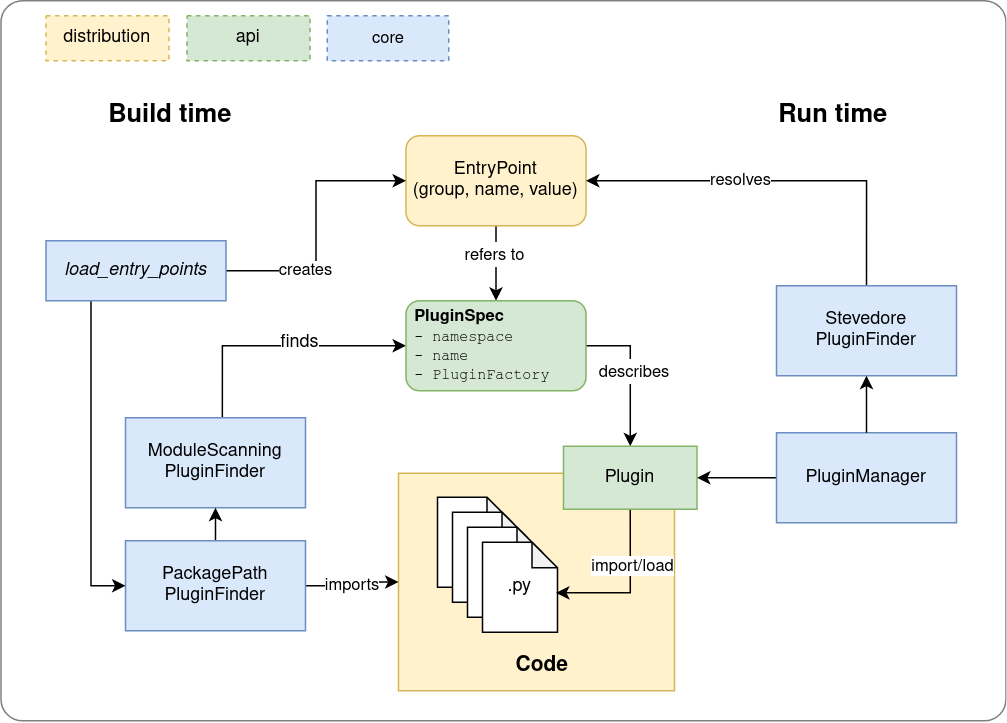
The plux builds a higher-level plugin mechanism around Python's entry point mechanism. It provides tools to load plugins from entry points at run time, and to discover entry points from plugins at build time (so you don't have to declare entry points statically in your setup.py).
Core concepts
PluginSpec: describes aPlugin. Each plugin has a namespace, a unique name in that namespace, and aPluginFactory(something that createsPluginthe spec is describing. In the simplest case, that can just be the Plugin's class).Plugin: an object that exposes ashould_loadandloadmethod. Note that it does not function as a domain object (it does not hold the plugins lifecycle state, like initialized, loaded, etc..., or other metadata of the Plugin)PluginFinder: finds plugins, either at build time (by scanning the modules usingpkgutilandsetuptools) or at run time (reading entrypoints of the distribution using stevedore)PluginManager: manages the run time lifecycle of a Plugin, which has three states:- resolved: the entrypoint pointing to the PluginSpec was imported and the
PluginSpecinstance was created - init: the
PluginFactoryof thePluginSpecwas successfully invoked - loaded: the
loadmethod of thePluginwas successfully invoked
- resolved: the entrypoint pointing to the PluginSpec was imported and the
Loading Plugins
At run time, a PluginManager uses a PluginFinder that in turn uses stevedore to scan the available entrypoints for things that look like a PluginSpec. With PluginManager.load(name: str) or PluginManager.load_all(), plugins within the namespace that are discoverable in entrypoints can be loaded. If an error occurs at any state of the lifecycle, the PluginManager informs the PluginLifecycleListener about it, but continues operating.
Discovering entrypoints
At build time (e.g., with python setup.py develop/install/sdist), a special PluginFinder collects anything that can be interpreted as a PluginSpec, and creates from it setuptools entrypoints. In the setup.py we can use the plugin.setuptools.load_entry_points method to collect a dictionary for the entry_points value of setup().
from plugin.setuptools import load_entry_points
setup(
entry_points=load_entry_points(exclude=("tests", "tests.*",))
)
Note that load_entry_points will try to resolve a cached version of entry_points.txt from the .egg-info directory, to avoid resolving the entry points when building the package from a source distribution.
Examples
To build something using the plugin framework, you will first want to introduce a Plugin that does something when it is loaded. And then, at runtime, you need a component that uses the PluginManager to get those plugins.
One class per plugin
This is the way we went with LocalstackCliPlugin. Every plugin class (e.g., ProCliPlugin) is essentially a singleton. This is easy, as the classes are discoverable as plugins. Simply create a Plugin class with a name and namespace and it will be discovered by the build time PluginFinder.
# abstract case (not discovered at build time, missing name)
class CliPlugin(Plugin):
namespace = "my.plugins.cli"
def load(self, cli):
self.attach(cli)
def attach(self, cli):
raise NotImplementedError
# discovered at build time (has a namespace, name, and is a Plugin)
class MyCliPlugin(CliPlugin):
name = "my"
def attach(self, cli):
# ... attach commands to cli object
now we need a PluginManager (which has a generic type) to load the plugins for us:
cli = # ... needs to come from somewhere
manager: PluginManager[CliPlugin] = PluginManager("my.plugins.cli", load_args=(cli,))
plugins: List[CliPlugin] = manager.load_all()
# todo: do stuff with the plugins, if you want/need
# in this example, we simply use the plugin mechanism to run a one-shot function (attach) on a load argument
Re-usable plugins
When you have lots of plugins that are structured in a similar way, we may not want to create a separate Plugin class for each plugin. Instead we want to use the same Plugin class to do the same thing, but use several instances of it. The PluginFactory, and the fact that PluginSpec instances defined at module level are discoverable (inpired by pluggy), can be used to achieve that.
class ServicePlugin(Plugin):
def __init__(self, service_name):
self.service_name = service_name
self.service = None
def should_load(self):
return self.service_name in config.SERVICES
def load(self):
module = importlib.import_module("localstack.services.%s" % self.service_name)
# suppose we define a convention that each service module has a Service class, like moto's `Backend`
self.service = module.Service()
def service_plugin_factory(name) -> PluginFactory:
def create():
return ServicePlugin(name)
return create
# discoverable
s3 = PluginSpec("localstack.plugins.services", "s3", service_plugin_factory("s3"))
# discoverable
dynamodb = PluginSpec("localstack.plugins.services", "dynamodb", service_plugin_factory("dynamodb"))
# ... could be simplified with convenience framework code, but the principle will stay the same
Then we could use the PluginManager to build a Supervisor
class Supervisor:
manager: PluginManager[ServicePlugin]
def start(self, service_name):
plugin = manager.load(service_name)
service = plugin.service
service.start()
Functions as plugins
with the @plugin decorator, you can expose functions as plugins. They will be wrapped by the framework into FunctionPlugin instances, which satisfy both the contract of a Plugin, and that of the function.
from plugin import plugin
@plugin(namespace="localstack.configurators")
def configure_logging(runtime):
logging.basicConfig(level=runtime.config.loglevel)
@plugin(namespace="localstack.configurators")
def configure_somethingelse(runtime):
# do other stuff with the runtime object
pass
With a PluginManager via load_all, you receive the FunctionPlugin instances, that you can call like the functions
runtime = LocalstackRuntime()
for configurator in PluginManager("localstack.configurators").load_all():
configurator(runtime)
Install
pip install plux
Develop
Create the virtual environment, install dependencies, and run tests
make venv
make test
Run the code formatter
make format
Upload the pypi package using twine
make upload